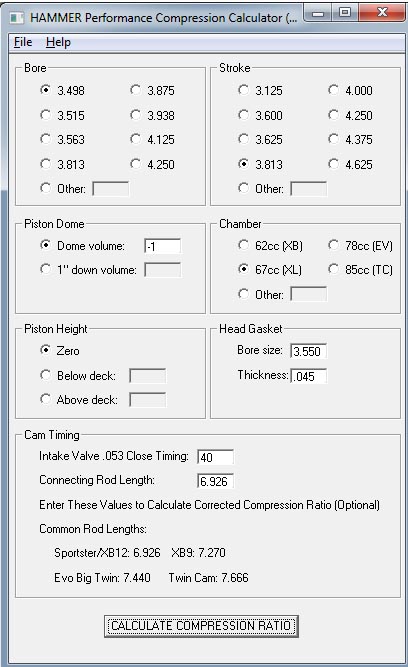
A tech article is to follow, but for now, click here to download a FREE copy of the HAMMER PERFORMANCE Compression Calculator (16KB).
Save it to your desktop or other convenient location and execute it.
This program calculates both static and corrected compression ratio. What's the difference? The static compression ratio takes the full compression stroke into account.
This is the standard way of doing it. The corrected compression ratio, however, only counts the portion of the compression stroke after the intake valve closes.
Since no compression builds until after the intake valve closes, it's the corrected compression ratio that gives the best indication of how pump gas friendly your motor will be. Premium pump
gas in the U.S. will generally tolerate corrected compression ratios of somewhere between 8.8:1 and 9.3:1. With a poor chamber that has little turbulence, stay on the low end of that range, maybe
even lower. With a good, turbulent chamber (think squish bands), you can run more toward the high end of the range. With good chamber turbulence and dual plugs, you can even run it higher, up to
9.5:1 is not unusual.
This tool gives progressively more information as you input more data:
- Displacement Only: Enter just the bore and stroke
- Displacement and Static Compression: Enter the bore, stroke, piston dome, chamber, piston height, and head gasket specs
- Displacement, Static Compression, and Corrected Compression: Enter data for all the fields
Here's an example of the full results:
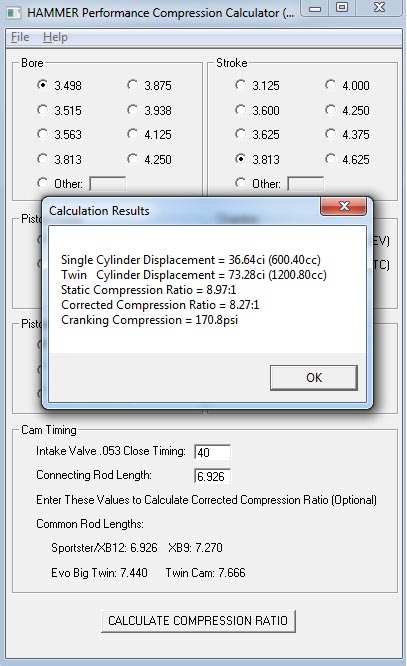
Shown Above with Results
This program was developed entirely in-house at HAMMER PERFORMANCE, and as delivered, contains no viruses or other malicious software. It simply does the calculations and gives you the results, nothing more.
Check back to this page for a much more detailed discussion of the subject.
Note that results given by this program are intended as a guideline only and HAMMER PERFORMANCE assumes no responsibility for what you do with the information presented.
|







